special tests for supraspinatus tear|empty can supraspinatus test explanation : distributors Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but confirmation requires an MRI of the shoulder.
Resultado da Eduardo Tega’s Post Eduardo Tega Founder & CSO na Sportheca ⚽ TEDx Speaker 2h Report this post Jornal mais lido do país, O Globo .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Jogo de dardos eletrônico com tela LCD ED110 Geologic. 4.2/5. (12) R$ 269,99. 5% cashback. 5x R$ 53,99. Vendido e entregue por Decathlon. REF: 8295138. Adicionar ao carrinho. Fale com um especialista. Frete e .
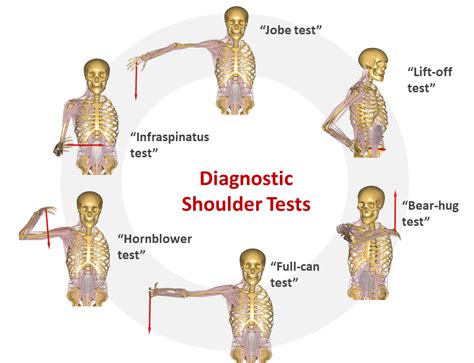
Traditionally Orthopaedic Special tests were used to assist in the diagnostic process by implicating specific tissue structures that are either dysfunctional, pathological, or lack structural integrity, confirming the findings from the physical assessment and providing a tentative diagnosis. Special testing . See moreHowever, although Orthopaedic Special Tests are commonly used, findings from both narrative, systematic reviews, and research investigations have consistently questioned the value of these procedures as a method of implicating the structures associated with . See more
shoulder tests for rotator cuff
Orthopaedic Special Tests may help us with symptom reproduction which can be used to test and retest following therapeutic interventions to assess for any change in symptoms. . See moreSpecial tests: [edit | edit source] Drop-arm test: Active shoulder abduction to 90°, then return [11] Positive: Dropping the arm down with pain indicates a positive testSupraspinatus Test. The supraspinatus tendon is the most frequently injured tendon of the rotator cuff. To test for integrity of the supraspinatus we can ask the patient to abduct both arms to 90° and then to bring them anteriorly with a 30° . Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but confirmation requires an MRI of the shoulder.
A combination of diagnostic tests for supraspinatus tendon tears including the empty can, full can, and the zero-degree abduction tests showed the best AUC (0.795) and hence the best diagnostic value.
In summary this study presents data on 15 commonly performed special tests for the rotator cuff and biceps tendon. This study provides evidence for high sensitivity and specificity of the . Rotator cuff special tests. A doctor or physiotherapist can use one of more than 25 functional tests during a physical exam to diagnosis a torn rotator cuff. Some of these tests directly.Each region of the body has a unique set of orthopaedic physical examination tests (“special tests”). In this Viewpoint, we focus on tests used to assess rotator cuf–related shoulder pain . A positive lag sign with external rotation is the best test for full-thickness tears of the infraspinatus and supraspinatus (positive likelihood ratio = 7.2). A positive lag sign with.
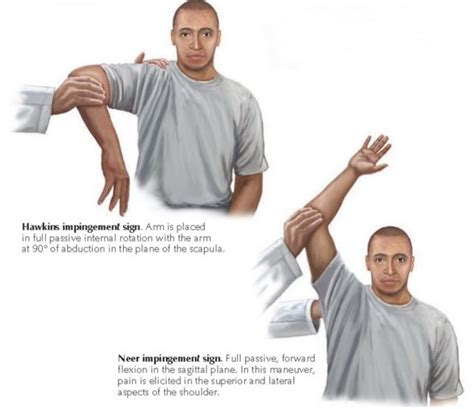
A combination of diagnostic tests for supraspinatus tendon tears including the empty can, full can, and the zero-degree abduction tests showed the best AUC (0.795) . The diagnostic accuracy of special tests for rotator cuff tear: the . The Neer sign and the Hawkins-Kennedy sign, commonly used to diagnose subacromial impingement, have a high sensitivity of 75–88% for supraspinatus tears.[18,19,20,21] However, these signs are characterized by a lack of specificity (<40%).[20,21] The transdeltoid palpation test, first described by Codman in 1934, has been used to diagnose .
The next rotator cuff tear special test that I perform is the drop arm test. The concept of this test is pretty similar to the shrug sign. . Sensitivity has varied in studies, but has shown 45-56% sensitivity to detect full thickness . This test targets one of the rotator cuff muscles that most commonly tears at the tendon: the supraspinatus. To perform the empty can test, fully extend your bad arm and raise it to shoulder height, slightly outward from your body. . Special Tests for Rotator Cuff Tear. Physical Therapists conduct special tests as part of their overall .Test Item Cluster: This test may be combined as a cluster with the Drop-Arm Sign and the Painful Arc Sign to test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. If all three tests report positive results, then the positive likelihood ratio is 15.6 and if all three tests are negative, the negative likelihood ratio is 0.16.
Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Empty Can Test, also known as the Jobe or Supraspinatus test, is used to assess for lesions of the rotator cuff, specifically the supraspinatus muscle and supraspinatus tendon.. Technique [edit | edit source]. The patients arm is actively abducted to 90 o; The examiner applies downward resistance to the abducted arm; With the patient's hand in . Primary care, sports medicine, and orthopedic surgeons commonly manage shoulder injuries and shoulder pain. Some reports in the literature cite that up to half of the clinical shoulder complaints are handled in a single visit by a primary care provider.[1] Rotator cuff pathologies are one common source of shoulder complaints. The rotator cuff consists of four . Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.Purpose: The purpose of this study was to analyze the diagnostic value of 7 clinical tests for the diagnosis of supraspinatus tendon tears, to investigate the ability of these tests to distinguish between partial- and full-thickness tears, and to compare 3 different ways of interpreting positive test results (weakness and pain): (1) in case of pain, (2) in case of weakness, regardless if with .
Empty Can test (p. 310) Supraspinatus - Pt standing, arm abducted to 90 deg, full IR and horizontally abducted ~30 degrees. - Thumbs should be pointed down - Therapist applies resistance to elevation (+) test = pain and/or weakness Drop Arm test (p. 313) Supraspinatus - Pt standing - Therapist abducts pt’s shld to 90 deg and - Apley scratch tests - Supraspinatus isometric strength test . - Internal lag test for rotator cuff tear - External lag test for rotator cuff tear - Neer test for shoulder impingement - Hawkins Kennedy test for shoulder impingement - Scapular repositioning test - Scapular . including many special tests designed to detect particular lesions .tests (“special tests”). In this Viewpoint, we focus on tests used to assess rotator cuff–related shoulder pain (RCRSP) (an . full-thickness supraspinatus tears and glenohumeral osteoarthritis had a 10% higher incidence in symptomatic shoul-ders.1 Magnetic resonance imaging and Introduction. Shoulder pain is one of the most common musculoskeletal disorders. The incidence of shoulder disorders was predicted at 11.2/1000 patients/year, with most cases originating from rotator cuff tears [1-3], which are usually due to subacromial impingement syndrome (SIS).SIS is the most common pathology that causes shoulder pain, and the .
Definition/Description [edit | edit source] Supraspinatus tendinopathy is a common and disabling condition that becomes more prevalent after middle age and is a common cause of shoulder pain.A predisposing factor is resistive overuse.. The supraspinatus tendon of the rotator cuff is involved and affected tendons of the musculoskeletal system and becomes degenerated, most .
Supraspinatus Tests. Supraspinatus Strength. strength is assessed using Jobe’s Test (see below) – pain with this test is indicative of a subacromial bursitis/irritation – not necessarily a tear. Only considered positive for tear with a true drop arm. i.e. arm is brought to 90° and literally falls down. . most specific test for full . Imaging tests may include: X-rays. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential causes for your pain — such as arthritis. Ultrasound. This type of test uses sound waves to produce images of structures within your body, particularly soft tissues such as muscles and tendons.
Sensitive tests include: Compression rotation test; O’Briens test; Apprehension Test; Specific tests include: Speed’s test; Yergason’s test; Biceps load test II; If one of the three tests is positive, this will result in a sensitivity of about 75%. .Jobe test and full can test had high sensitivity and specificity for supraspinatus tears, and Hornblower sign performed well for infraspinatus tears. In general, special tests described for subscapularis tears have high specificity but low sensitivity. These data .
shoulder special tests rotator cuff
Special Tests for the Supraspinatus (1) Full Can / Empty Can Test: . This test indicates if a rotator cuff tear is present however i t is not specific to the supraspinatus. The physiotherapist supports the weight of the patients arm out in an abducted position and then releases it slowly. If the rotator cuff is injured, weakness will result .Weakness can be the result of a tear in the supraspinatus muscle or tendon but can also be the result of pain induced inhibition. Pain is usually felt in the subacromial region but can sometimes be felt into the upper arm. . Special Tests for Orthopedic Examination, now in its Fourth Edition, continues to follow the authors’ initial goals . Speed's test is a special test meant to identify tendonitis in your bicep. The bicep muscle has two tendons that connect it to the shoulder bone. . Pain or weakness indicates a positive test for a possible supraspinatus tear or problem. Tests for Frozen Shoulder . A frozen shoulder is defined by a severe loss of range of motion in a quite .
Special Tests/Assess; Full and Empty Can Test; Related Pages. . The examiner provides downward pressure to test the patient’s strength in this position. A positive test for rotator cuff tear is more weakness in the empty can, patient complaint of pain, or both. . Razmjou H. Validity of the supraspinatus test as a single clinical test in . To provide guidance, Jon J.P. Warner, MD, chief of the Shoulder Service at Massachusetts General Hospital, and colleagues compared the diagnostic accuracy of 15 special tests. In the American Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, they report that the Jobe test and "full can test" performed well for diagnosis of supraspinatus tears, and the .

ONLINE COURSES: https://study.physiotutors.comGET OUR ASSESSMENT BOOK ︎ ︎ http://bit.ly/GETPT ︎ ︎OUR APPS: 📱 iPhone/iPad: https://apple.co/35vt8Vx🤖 Andro. Sensitivity & Specificity. A literature review 1 in MEDLINE was performed for physical examination tests/maneuvers of the rotator cuff tears, and found that drop arm sign has the following accuracy:. Sensitivity: 73 %; Specificity: 98 %; Another study by Walch G 2 found that this test has a 100% sensitivity and a 100% specificity for irreparable degeneration of the . Finally, the “painful arc sign” has high sensitivity (97.5 percent) as a single finding, making it helpful in ruling out rotator cuff tears when absent. 2 The test is performed by having the .Special tests. There are multiple special tests for the shoulder, . For detecting a supraspinatus tear the test has a sensitivity of 18.7% and a specificity of 100%, 4 this means if the test is positive it is highly likely that the patient has a tear. The second test is the Drop arm test. In this test the patient's arm is abducted to at least .
ferrex feuchtigkeitsmessgerät bedienungsanleitung
rotator cuff tear physical exam
WEB28 de jul. de 2014 · $10 - $12. CUISINES. Steakhouse, Brazilian, Barbecue, South American, Sushi. Meals. Lunch, Dinner. View all details. features. .
special tests for supraspinatus tear|empty can supraspinatus test explanation